- What is Vulnerability Scanning?
- How Does Vulnerability Scanning Work?
- Vulnerability Scanning Statistical Insights
- What is Penetration Testing?
- How Does Penetration Testing Work?
- Penetration Testing Statistical Insights
- Key Differences Between Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
- Depth and Scope
- Automation vs. Manual Effort
- Frequency and Timing
- Output and Reporting
- Practical Benefits of Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
- Benefits of Vulnerability Scanning
- Benefits of Penetration Testing
- When to Use Vulnerability Scanning vs. Penetration Testing
- Scenarios for Vulnerability Scanning
- Scenarios for Penetration Testing
Cybersecurity is no longer an option but a necessity for businesses of all sizes. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks make it essential to identify and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited. Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are two critical tools in the cybersecurity toolkit, each playing a distinct role in safeguarding your digital assets. There is often confusion between vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
What is Vulnerability Scanning?
Basically, it automates the process of vulnerability scanning, offering a good view of potential security weaknesses in the network, system or application. Scans run over known vulnerabilities, including outdated software, misconfigurations and missing patches, to come up with a definite list of security gaps that are to be remediated.
How Does Vulnerability Scanning Work?
Vulnerability Scanning is a special software-oriented scan that is conducted about weaknesses in the system. A scanner inspects the system’s condition by comparing it with a known database of weaknesses and noting where something deviates from said database. Scans of this nature may conduct frequently to ensure continuity in security.
Vulnerability Scanning Statistical Insights
According to a 2023 report by Security.org, over 60% of organizations use vulnerability scanning as part of their regular security practices. Additionally, automated scanning tools identify 85% vulnerabilities (it highlights their importance in early detection).
What is Penetration Testing?
Basically, hacking essentially carried out under controlled conditions is penetration testing, in which a company’s computer systems simulate for a cyber attack to reveal weaknesses that can be exploited. Penetration test takes it beyond merely scanning for possible vulnerabilities: researchers use automated tools and manual techniques to mimic the tactics employed by real-world aggressors.
How Does Penetration Testing Work?
Above all, security experts perform penetration tests to uncover weaknesses in a secure setting. They simulate a cyber attack to reveal potential entry points for unauthorized access and utilize various tools and methods for this.
Penetration Test Statistical Insights
A study by the Ponemon Institute in 2022 found that 78% of organizations that conduct regular penetration tests report a significant improvement in their security posture. Furthermore, automated scanning alone did not identify critical vulnerabilities in 90% of the cases, but pen test did.
Penetration Testing vs Vulnerability Scanning
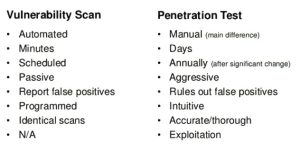
So, what is the main difference between vulnerability scanning and penetration testing?
Depth and Scope
- Vulnerability Scanning is broad and shallow. It covers a wide range of vulnerabilities but does not provide detailed insights into how they can be exploited.
- Penetration Testing is narrow and deep. It focuses on specific vulnerabilities and provide detailed information on how they can be exploited and the potential impact.
Automation vs. Manual Effort
- Vulnerability Scanning primarily automated and require minimal human intervention.
- Penetration Testing combines automated tools with manual testing, involve significant human expertise.
Regularity and Schedule
- Vulnerability Scanning is regular and frequent, often performed weekly or monthly.
- Penetration Testing is periodic, typically conducted annually or after significant changes to the system.
Output and Report
- Vulnerability Scanning generates a comprehensive list of vulnerabilities with remediation suggestions.
- Penetration Testing provides detailed reports, include exploitation techniques, potential impact, and strategic recommendations for improving security.
Benefits of Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
Vulnerability Scanning Benefits
- Early Detection quickly identifies vulnerabilities, allowing for prompt remediation.
- Cost-Effective automated nature makes it a cost-effective option for regular security assessments.
- Comprehensive Coverage scans a broad range of systems and applications.
Penetration Testing Benefits
- Real-World Insights mimics actual attack scenarios, provide realistic insights into potential threats.
- Detailed Analysis offers an in-depth analysis of vulnerabilities and their exploitability.
- Enhanced Security Posture helps to identify and address critical weaknesses that may not be detected by automated scans.
When to Use Vulnerability Scanning vs. Penetration Testing
Scenarios for Vulnerability Scanning
- Routine Security Checks: Ideal for regular assessments to maintain a secure baseline.
- Compliance Requirements: Often required for compliance with standards like PCI-DSS and HIPAA.
- Resource Constraints: Suitable for organizations with limited cybersecurity resources.
Scenarios for Penetration Testing
- High-Risk Environments: Essential for organizations with high-value assets or sensitive data.
- Post-Deployment: Important after major system updates or deployments to ensure security.
- Advanced Threat Detection: Useful for identifying sophisticated threats that automated tools might miss.
So, vulnerability assessment vs penetration test? Both vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are vital components of a robust cybersecurity strategy. While vulnerability scanning offers a broad overview of potential security gaps, penetration test provides a deeper, more nuanced grasp of how these vulnerabilities can be exploited. Organizations can ensure comprehensive protection against cyber threats if combine both methods.
Accordingly, with attention to understand the main differences and practical benefits of these security practices, businesses can better protect themselves against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Whether you’re performing regular vulnerability scans or conducting in-depth penetration tests, staying proactive in your cybersecurity efforts is the key to maintaining a secure and resilient digital environment.
Read also interesting article about “Why is a quality assurance tester needed on a software development team?“.